Galgame汉化中的逆向(八)_哈希算法分析_以krkrz_hxv4为例
之前我几篇hxv4还原计划,由于很多人对于hxv4不是很了解,故也将此贴发到这里绯月, 用于科普。 【游戏解包】DC5PH_D.C.5PlusHappiness_初音岛5 (HXV4还原计划1)https://www.kungal.com/topic/1939 【游戏解包】DC5SH_D.C.5 Sweet Happiness_初音岛5FD(HXV4还原计划2)https://www.kungal.com/topic/2767 【游戏解包】DC1RE_D.C. Re:tune_初音岛1RE(HXV4还原计划3)https://www.kungal.com/topic/2823
这几年ai迅速发展,使得逆向分析门槛大幅下降。若依赖ai反而会觉得缺少乐趣,亦或是和ai扯皮半天,ai还睁眼说瞎话,你纠正错误到面红耳赤,它反手给你甩个“you reached rate limit”强行结束。逆向作为茶余饭后之娱乐活动,就和我们喜欢手动挡一样,完全由自己掌控的心流令人欲罢不能。本文将不依赖ai, 依旧以传统的逆向方法和技巧来呈现。
时隔三年再次发帖,提前祝大家新年快乐~
by devseed
0x0 background
近些年,wamsoft魔改的krkrz引入了hxv4解密方案,最大的区别是封包只存储文件哈希值,不存储文件名。游戏脚本(通常为*.scn)内资源文件以原始文件名存储,引擎运行时计算得到哈希值,从而找到封包内对应文件。由于哈希函数不可逆,这使得要想得到文件名变得非常麻烦(要么你得跑一边游戏所有分支剧情dump,或者干脆不要文件名了)。
目前主要有两种方案,运行时dump(krkrdump)、扫描对应的脚本构建字符串碰撞从而得到哈希值和文件名的映射(KrkrExtractForCxdecV2+krkr_hxv4_dumphash)。本文将以dc5ph为例分析hxv4的哈希函数,以及如何还原对应的算法和数据结构。
0x1 krkrz、hxv4
直接分析hxv4则是非常困难的,可以通过原版krkrz了解引擎大概加载流程,再针对性的进行寻找,原版Stream如下:
tTVPPlugin -> TVPCreateIStream -> _TVPCreateStream -> tTVPArchive::CreateStream -> TVPStorageMediaManager.Open -> tTVPXP3Archive::CreateStreamByIndex -> Read
关于hxv4,可以参考hxcrypt。Hxv4entry内容是加密的,先解密这个entry,之后得到filter key在用旧版cxdec方法解密各个文件entry。如下:
// decrypt hxv4 index
Xp3Stream::TryOpen -> HxCrypt::ReadIndex -> HxChachaDecryptor::Decrypt
// decrypt file content
HxFilter::Decrypt -> HxFilterSpan::DecryptHeader
解密相关参数示例如下,获取方式可以用我写的firda脚本krkr_hxv4_dumpkey。
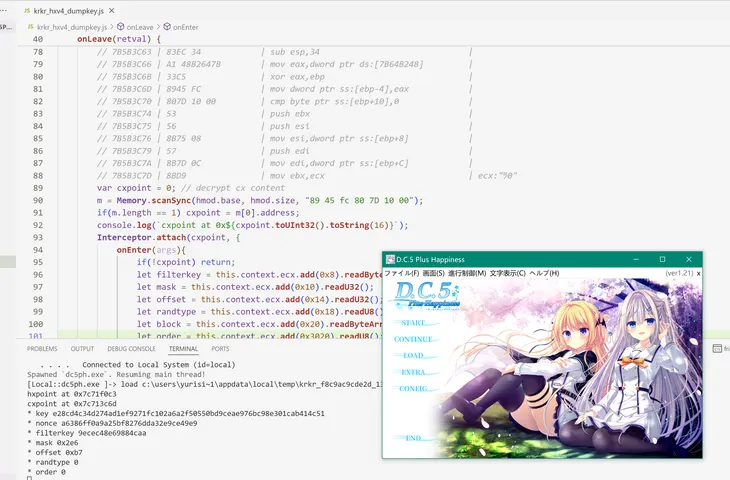
control_block.bin // 4096 bytes
hxpoint at 0x5b18f0c3
cxpoint at 0x5b183c6d
* key : b338a06fc12ba33610e7e4428c8389ca0342b418ae6a77e5287e3607e41fe65b
* nonce : ec668fc7eff5f388612eb56f1e6d4d6f
* filterkey : 4eef61df5f2e1771
* mask : 0x273
* offset : 0x178
* randtype : 1
* order : 04 00 02 03 06 01 07 05 04 05 00 01 03 02 00 02 01
* PrologOrder (garbro) : 0, 2, 1
* OddBranchOrder (garbro) : 3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 5
* EvenBranchOrder (garbro) : 2, 6, 3, 1, 0, 4, 5, 7
\## 0x2 program flow
分析的切入点结合krkrz源码是虚函数的RTTI,找到关键函数\`v2link\`, \`tTVPXP3ArchiveStream\`。找到此函数,即可调用read函数将其文件动态dump出来。
\`\`\` text
.rdata:00728520 ; class tTVPXP3ArchiveStream: TJS::tTJSBinaryStream; (#classinformer)
.rdata:00728520 dd offset ??\_R4tTVPXP3ArchiveStream@@6B@ ; const tTVPXP3ArchiveStream::\`RTTI Complete Object Locator'
.rdata:00728524 ; const tTVPXP3ArchiveStream::\`vftable'
.rdata:00728524 ??\_7tTVPXP3ArchiveStream@@6B@ dd offset tTVPXP3ArchiveStream\_\_Seek\_437230
.rdata:00728524 ; DATA XREF: sub\_436D90+41↑o
.rdata:00728524 ; sub\_436E90+2A↑o
.rdata:00728528 dd offset tTVPXP3ArchiveStream\_\_Read\_4372E0
.rdata:0072852C dd offset sub\_402CD0
.rdata:00728530 dd offset sub\_4768F0
.rdata:00728534 dd offset tTVPXP3ArchiveStream\_\_GetSize\_437480
.rdata:00728538 dd offset tTVPXP3ArchiveStream\_\_deconstruct\_436E60
\`\`\`
如果没有RTTI,则可以通过函数特征码定位(一般来说编译器变化不大的情况下,生成对应函数的代码差不多,所以可以自己编译一下,看看对应函数代码什么样)。\`TVPCreateStream\`函数和对应的代码如下。这个函数找到后继续跟\`TVPStorageMediaManager::Open\_40CFD0\`函数顺藤摸瓜找到hxv4相关函数。不同于传统的\`krkrz filter\`解密函数,hxv4通过\`StorageMediaManager\`对stream接管很早。
\`\`\` text
.text:0040EDB0 ; =============== S U B R O U T I N E =======================================
.text:0040EDB0
.text:0040EDB0 ; signature: 55 8b ec 6a ff 68 ? ? ? ? 64 a1 ? ? ? ? 50 83 ec 5c 53 56 57 a1 ? ? ? ? 33 c5 50 8d 45 f4 64 a3 ? ? ? ? 89 65 f0 89 4d ec c7 45 ? ? ? ? ? e8 ? ? ? ? 8b 4d f4 64 89 0d ? ? ? ? 59 5f 5e 5b 8b e5 5d c3
.text:0040EDB0 ; void \*\_\_fastcall TVPCreateStream\_40EDB0(void \*name, uint32\_t flags)
.text:0040EDB0 \_TVPCreateStream\_40EDB0 proc near ; CODE XREF: TVPCreateStream\_40F040+35↓p
.text:0040EDB0
.text:0040EDB0 ; \_\_unwind { // SEH\_40EDB0
.text:0040EDB0 55 push ebp
.text:0040EDB1 8B EC mov ebp, esp
.text:0040EDB3 6A FF push 0FFFFFFFFh
.text:0040EDB5 68 C8 9F 69 00 push offset SEH\_40EDB0
.text:0040EDBA 64 A1 00 00 00 00 mov eax, large fs:0
.text:0040EDC0 50 push eax
.text:0040EDC1 83 EC 24 sub esp, 24h
.text:0040EDC4 53 push ebx
.text:0040EDC5 56 push esi
.text:0040EDC6 57 push edi
.text:0040EDC7 A1 50 F9 76 00 mov eax, \_\_\_security\_cookie
.text:0040EDCC 33 C5 xor eax, ebp
.text:0040EDCE 50 push eax
.text:0040EDCF 8D 45 F4 lea eax, \[ebp+var\_C]
.text:0040EDD2 64 A3 00 00 00 00 mov large fs:0, eax
.text:0040EDD8 89 65 F0 mov \[ebp+var\_10], esp
.text:0040EDDB 8B DA mov ebx, edx
.text:0040EDDD 89 5D DC mov \[ebp+flags\_alter1], ebx
.text:0040EDE0 8B F9 mov edi, ecx
.text:0040EDE2 C7 45 D4 84 64 78 mov \[ebp+var\_2C], offset stru\_786484
.text:0040EDE2 00
.text:0040EDE9 68 84 64 78 00 push offset stru\_786484 ; lpCriticalSection
.text:0040EDEE FF 15 24 03 6C 00 call ds:EnterCriticalSection
.text:0040EDF4 ; try {
.text:0040EDF4 C7 45 FC 00 00 00 mov \[ebp+var\_4], 0
.text:0040EDF4 00
.text:0040EDFB C7 45 EC 00 00 00 mov \[ebp+name\_alter1], 0
\`\`\`
调试后可知hxv4的dll藏在exe资源文件中,去hook\`LoadlibraryW\`后可知他会在C盘生成类似于\`krkr\_xxx/yyy.dll\`,hxv4相关的文件解密还有哈希函数都在里面,切入点如下:
\`\`\`text
.rdata:1008199C ; struct struct DefaultCompoundHasher\<PathNameHashTrait>: struct CompoundStringHasher; (#classinformer)
.rdata:1008199C F4 6B 09 10 dd offset ??\_R4?\$DefaultCompoundHasher\@UPathNameHashTrait@@@@6B@ ; const DefaultCompoundHasher\<PathNameHashTrait>::\`RTTI Complete Object Locator'
.rdata:100819A0 ; const DefaultCompoundHasher\<struct PathNameHashTrait>::\`vftable'
.rdata:100819A0 C0 67 01 10 ??\_7?\$DefaultCompoundHasher\@UPathNameHashTrait@@@@6B@ dd offset au\_re\_j\_\_free\_0\_12
.rdata:100819A0 ; DATA XREF: sub\_10016680+2B↑o
.rdata:100819A0 ; deconstructor
.rdata:100819A4 F0 69 01 10 dd offset DirHashCompute\_100169F0
.rdata:100819A8
.rdata:100819A8 ; struct struct DefaultCompoundHasher\<FileNameHashTrait>: struct CompoundStringHasher; (#classinformer)
.rdata:100819A8 40 6C 09 10 dd offset ??\_R4?\$DefaultCompoundHasher\@UFileNameHashTrait@@@@6B@ ; const DefaultCompoundHasher\<FileNameHashTrait>::\`RTTI Complete Object Locator'
.rdata:100819AC ; const DefaultCompoundHasher\<struct FileNameHashTrait>::\`vftable'
.rdata:100819AC 80 67 01 10 ??\_7?\$DefaultCompoundHasher\@UFileNameHashTrait@@@@6B@ dd offset au\_re\_j\_\_free\_0\_11
.rdata:100819AC ; DATA XREF: sub\_10016580+2B↑o
.rdata:100819B0 00 69 01 10 dd offset FileHashCompute\_10016900
00000000 struct IStringHasher\_VptrTable // sizeof=0x8
00000000 {
00000000 void \*Destruct;
00000004 void \*Calculate;
00000008 };
00000000 struct IStringHasher // sizeof=0xC
00000000 {
00000000 IStringHasher\_VptrTable \*VptrTable;
00000004 uint8\_t \*salt;
00000008 int saltsize;
0000000C };
\`\`\`
从切入点顺藤摸瓜,可以归纳出下列数据结构和行为逻辑:
\`\`\` c
typedef tjs\_int(\_\_fastcall \*FuncHxv4CalcHash)(Hxv4CompoundHasher\* \_this, void\* \_edx, 
  OUT tTJSVariant\* hash, const tTJSString\* str, const tTJSString\* seed);
typedef struct Hxv4CompoundHasher
{
  struct 
  {
  void\* destruct;
  FuncHxv4CalcHash calc;
  } \*vftable; // offset 0
  tjs\_uint8\* salt; // offset 0x4
  tjs\_int saltsize; // offset 0x8
} Hxv4CompoundHasher;
typedef struct Hxv4DirHasher
{
  Hxv4CompoundHasher base;
  tjs\_uint8 saltdata\[0x10];
} Hxv4DirHasher;
typedef struct Hxv4FileHasher
{
  Hxv4CompoundHasher base;
  tjs\_uint8 saltdata\[0x20];
} Hxv4FileHasher;
typedef struct Hxv4CompoundStorageMedia
{
  void\* vftable;
  int nref;
  uint32\_t reserve1;
  tTJSString prefix; 
  tTJSString seed; //offset 0x10
  CRITICAL\_SECTION critical\_section;
  uint8\_t reserve2\[0x20];
  tTJSString\* start;
  tTJSString\* pos;
  tTJSString\* end;
  Hxv4DirHasher\* dirhasher; // offset 0x58
  Hxv4FileHasher\* filehasher;
} Hxv4CompoundStorageMedia;
// hook from here
unsigned int \_\_cdecl CreateCompoundStorageMedia\_100059D0(
  CompoundStorageMedia \*\*retTVPStorageMedia,
  int tjsVarPrefix,
  int argc,
  int \*argv)
{
  ...
  if ( argc > 1 ) CompoundStorageMedia::Init\_1000A3D0(\*retTVPStorageMedia, 0, \*argv, argv\[1]);
  ...
  \*retTVPStorageMedia = v10;
  TVPRegisterStorageMedia\_100068C0(v10); // in exe it will tTVPStorageMediaManager::Open
  ...
}
int \_\_thiscall CompoundStorageMedia::Init\_1000A3D0(CompoundStorageMedia \*this, int a2, void \*seed\_variant, size\_t Size)
{
  ...
  this->PathNameHasher = (IStringHasher \*)PathNameHasher::Init\_10016890(Size);
  this->FileNameHasher = (IStringHasher \*)FileHasher::Init\_10016820(Size);
  ...
}
\`\`\`
至此我们已经找到了哈希函数了,可以动态附加到游戏程序里,直接调用\`Hxv4CompoundHasher::vftable->calc\`来计算任意字符串,详见\[krkr\_hxv4\_dumphash]\(https\://github.com/YuriSizuku/GalgameReverse/blob/master/project/krkr/src/krkr\_hxv4\_dumphash.cpp)。
\## 0x3 hash function
动态dump hash后,更进一步,我们要怎么分析算法逻辑,并且能够静态复现呢?最笨的方法是直接把相关逻辑的C伪代码或者汇编代码搬出来,逐个模拟实现(汇编可用unicorn模拟)。但是这种方法费时费力,一个哈希函数动辄上千行,还特别容易出错。所以去年分析到动态调用这一步就没再继续,最近看了看发现可以从特征进行分析,从而得以继续。
站在开发者的角度想,大部分游戏不会自己研制一套全新的哈希算法,大多数是用现有的方法,或者在现有的方法上改改参数或流程。因此我们还原算法的主要目标,是寻找当前算法是哪个原有算法的改版。那么哈希算法如何进行呢?通常是下面几个步骤:
\`init(key, salt) -> update(buf, lastvalue) -> final(outsize)\`
还原哈希算法,函数的输入输出还有函数内相关常数需要重点关注。本游戏有两种哈希算法,计算文件名的hash、计算文件夹的hash。
\### file hash
计算文件哈希算法如下,\`tTJSString\`使得此函数变得很乱, 移除掉后可以很清晰的看到计算哈希的流程。输入为文本unicode编码,输出为32字节。之前动态调用计算得到一组值为\`!scnlist.txt,C1F625E3A4BB508E082A52A8B032F4B3D2F34FF7FB3A30502574717DE6579126\`。
filehash\_init\_1000E070 -> filehash\_update\_100159F0 -> filehash\_final32\_10016B00
\`\`\` c
int \_\_userpurge FileHashCompute\_10016900@\<eax>(
  IStringHasher \*this@\<ecx>,
  void \*hashValueRet,
  tTJSString\_S \*rawstr,
  tTJSString\_S \*seed)
{
  size\_t (\_\_stdcall \*v4)(tTJSString\_S \*); // eax
  int (\_\_stdcall \*v5)(tTJSString\_S \*); // eax
  uint8\_t \*raw\_cstr; // eax
  int (\_\_stdcall \*v7)(tTJSString\_S \*); // eax
  int seed\_len; // edi
  int (\_\_stdcall \*v9)(tTJSString\_S \*); // eax
  uint8\_t \*seed\_cstr; // eax
  size\_t v12; // \[esp-8h] \[ebp-94h]
  filehash\_ctx ctx; // \[esp+Ch] \[ebp-80h] BYREF
  filehash\_init\_1000E070(\&ctx, 0x20u, this->salt, this->saltsize);
  v4 = (size\_t (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))tTJSString::length\_100AD158;
  if ( !tTJSString::length\_100AD158 )
  {
  v4 = (size\_t (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))findfunc\_10016420((void (\_\_stdcall \*)(\_DWORD))aTjsIntTtjsstri);
  tTJSString::length\_100AD158 = (int)v4;
  }
  v4(rawstr);
  v5 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4;
  if ( !TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4 )
  {
  v5 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))findfunc\_10016420((void (\_\_stdcall \*)(\_DWORD))aConstTjsCharTt);
  TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4 = (int)v5;
  }
  raw\_cstr = (uint8\_t \*)v5(rawstr);
  filehash\_update\_100159F0(\&ctx, raw\_cstr, v12); // v12=2\*rawstr\_len
  if ( seed )
  {
  v7 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))tTJSString::length\_100AD158;
  if ( !tTJSString::length\_100AD158 )
  {
  v7 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))findfunc\_10016420((void (\_\_stdcall \*)(\_DWORD))aTjsIntTtjsstri);
  tTJSString::length\_100AD158 = (int)v7;
  }
  seed\_len = v7(seed);
  v9 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4;
  if ( !TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4 )
  {
  v9 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))findfunc\_10016420((void (\_\_stdcall \*)(\_DWORD))aConstTjsCharTt);
  TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4 = (int)v9;
  }
  seed\_cstr = (uint8\_t \*)v9(seed);
  filehash\_update\_100159F0(\&ctx, seed\_cstr, 2 \* seed\_len);
  }
  return filehash\_final32\_10016B00((int)\&ctx, hashValueRet);// return 32, fill hashvalueret
}
\`\`\`
这里我们重点关注\`filehash\_init\_1000E070\`其中的\`init\_filehash\_ctx\_10014140\`, 搜索立即数\`6A09E667h\`,可知这是\`sha256\`的table,其中\`blake2s\`算法也共用这个table。
\`\`\` c
filehash\_ctx \*\_\_thiscall filehash\_init\_1000E070(filehash\_ctx \*pctx, size\_t outlen, uint8\_t \*key, size\_t keylen)
{
  size\_t v5; // eax
  uint8\_t tmp\[32]; // \[esp+Ch] \[ebp-64h] BYREF
  uint8\_t tmp2\[64]; // \[esp+2Ch] \[ebp-44h] BYREF
  if ( outlen && outlen <= 0x20 && (key || !keylen) )
  {
  tmp\[0] = outlen;
  memset(\&tmp\[9], 0, 23);
  \*(\_QWORD \*)\&tmp\[1] = (unsigned \_\_int8)keylen;
  \*(\_WORD \*)\&tmp\[2] = 0x101;
  sub\_10014260((uint8\_t \*)pctx, tmp);
  if ( key && keylen )
  {
  memset(tmp2, 0, sizeof(tmp2));
  v5 = 64;
  if ( keylen < 64 )
  v5 = keylen;
  memmove\_0(tmp2, key, v5);
  filehash\_update\_100159F0(pctx, tmp2, 0x40u);
  memset(tmp2, 0, sizeof(tmp2));
  }
  }
  else
  {
  init\_filehash\_ctx\_10014140(pctx); // init filehash iv
  }
  return pctx;
}
.text:10014140 ; void \*\_\_thiscall init\_filehash\_ctx\_10014140(filehash\_ctx \*pctx)
.text:10014140 ; sub\_10010410+F5↑p ...
.text:10014140 push esi
.text:10014141 mov esi, ecx
.text:10014143 push 40h ; '@' ; Size
.text:10014145 mov dword ptr \[esi], 6A09E667h
.text:1001414B mov dword ptr \[esi+4], 0BB67AE85h
.text:10014152 mov dword ptr \[esi+8], 3C6EF372h
.text:10014159 mov dword ptr \[esi+0Ch], 0A54FF53Ah
.text:10014160 mov dword ptr \[esi+10h], 510E527Fh
.text:10014167 mov dword ptr \[esi+14h], 9B05688Ch
.text:1001416E mov dword ptr \[esi+18h], 1F83D9ABh
.text:10014175 mov dword ptr \[esi+1Ch], 5BE0CD19h
.text:1001417C lea eax, \[esi+30h]
.text:1001417F push 0 ; Val
.text:10014181 mov dword ptr \[esi+20h], 0
.text:10014188 mov dword ptr \[esi+24h], 0
.text:1001418F mov dword ptr \[esi+28h], 0
.text:10014196 mov dword ptr \[esi+2Ch], 0
.text:1001419D push eax ; void \*
.text:1001419E mov eax, ds:off\_10080BD4
.text:100141A3 call eax ; \_memset
.text:100141A5 add esp, 0Ch
.text:100141A8 mov dword ptr \[esi+70h], 0
.text:100141AF mov dword ptr \[esi+74h], 0
.text:100141B6 mov byte ptr \[esi+78h], 0
.text:100141BA pop esi
.text:100141BB retn
\`\`\`
这时候就大胆假设小心求证了, 把\`blake2s\`的结构放进去看看能不能成立。经测试,这个和原版的\[blake2s]\(https\://github.com/secworks/blake2s/blob/master/src/model/blake2s.c)结构体布局略有区别(input缓存和pos跑到下面了,并且多了个pos),如下结构体是能对上的。
\`\`\` c
struct filehash\_ctx
{
  uint32\_t h\[8]; // chained state
  uint32\_t t\[2]; // total number of bytes
  size\_t c; // pointer for b\[]
  size\_t outlen; // digest size
  uint8\_t b\[64]; // input buf
  uint32\_t pos;
};
void \*\_\_thiscall filehash\_update\_100159F0(filehash\_ctx \*pctx, uint8\_t \*src)
{
  uint8\_t \*v2; // ebx
  size\_t v4; // edi
  uint32\_t pos; // ecx
  void \*result; // eax
  uint32\_t Srca; // \[esp+10h] \[ebp+8h]
  uint8\_t \*Srcb; // \[esp+10h] \[ebp+8h]
  size\_t srcsize; // \[esp+14h] \[ebp+Ch]
  v2 = src;
  if ( src )
  {
  v4 = srcsize;
  if ( srcsize )
  {
  pos = pctx->pos;
  result = (void \*)(64 - pos);
  Srca = 64 - pos;
  if ( srcsize > 64 - pos )
  {
  memmove\_0(\&pctx->b\[pos], v2, 64 - pos);
  pctx->t\[0] += 64;
  pctx->t\[1] += pctx->t\[0] < 0x40;
  result = (void \*)filehash\_compress\_10012500(pctx, (int)pctx->b);
  v4 = srcsize - Srca;
  v2 += Srca;
  if ( srcsize - Srca > 0x40 )
  {
  Srcb = (uint8\_t \*)(((v4 - 65) >> 6) + 1);
  do
  {
  pctx->t\[0] += 64;
  pctx->t\[1] += pctx->t\[0] < 0x40;
  result = (void \*)filehash\_compress\_10012500(pctx, (int)v2);
  v2 += 64;
  v4 -= 64;
  \--Srcb;
  }
  while ( Srcb );
  }
  pctx->pos = 0;
  }
  if ( v4 )
  {
  result = memmove\_0(\&pctx->b\[pctx->pos], v2, v4);
  pctx->pos += v4;
  }
  }
  }
  return result;
}
\`\`\`
\`filehash\_compress\_10012500\`函数超级长, 不过大概流程和\`blake2s\`也能对上。\`G\`操作里面一大堆\`ROTR32\`。
\`\`\`c
int \_\_thiscall filehash\_compress\_10012500(filehash\_ctx \*ctx, int last)
{
  ...
  v3 = 0;
  v4 = (unsigned \_\_int8 \*)(last + 2);
  do
  {
  \*(\&v663 + v3++) = \*(v4 - 2) | (unsigned \_\_int16)(\*(v4 - 1) << 8) | ((\*v4 | (unsigned \_\_int16)(v4\[1] << 8)) << 16);
  v4 += 4;
  }
  while ( v3 < 16 );
  v584 = \*(\_DWORD \*)\&ctx->h\[12];
  v5 = \*(\_DWORD \*)\&ctx->h\[16];
  v461 = \_\_ROL4\_\_((v5 + v663 + \*(\_DWORD \*)ctx->h) ^ \*(\_DWORD \*)\&ctx->h\[32] ^ 0x510E527F, 16);
  v6 = \*(\_DWORD \*)\&ctx->h\[20];
  v624 = v5 + v663 + \*(\_DWORD \*)ctx->h;
  v7 = v461 + 1779033703;
  v8 = \_\_ROR4\_\_(v5 ^ (v461 + 1779033703), 12);
  v462 = \_\_ROR4\_\_((v8 + v664 + v624) ^ v461, 8);
  v414 = v462 + v7;
  v343 = \_\_ROR4\_\_(v8 ^ (v462 + v7), 7);
  v529 = v6 + v665 + \*(\_DWORD \*)\&ctx->h\[4];
  v625 = v8 + v664 + v624;
  v9 = \_\_ROL4\_\_(v529 ^ \*(\_DWORD \*)\&ctx->h\[36] ^ 0x9B05688C, 16);
  ...
}
\`\`\`
至此我们已经确信, file hash大概率是基于\`blake2s\`的算法了,先不去详细分析上面那个巨长函数,先尝试一下是不是标准\`blake2s\`。很幸运,这个游戏并没有大改,salt为空,原版函数再加上\`xp3hnp\`的seed(动态调试得到的)即可搞定。
\`\`\`py
from hashlib import blake2s
h = blake2s(digest\_size=32)
h.update("!scnlist.txt".encode("utf-16le"))
h.update("xp3hnp".encode("utf-16le"))
print(h.hexdigest()) // c1f625e3a4bb508e082a52a8b032f4b3d2f34ff7fb3a30502574717de6579126
\`\`\`
\### dir hash
分析文件夹哈希与文件哈希方法类似。输出8字节,动态计算的一组值为\`ED,FEF68C92D344F4F6\`。
\`\`\` c
int \_\_userpurge DirHashCompute\_100169F0@\<eax>(
  IStringHasher \*this@\<ecx>,
  void \*hashValueRet,
  tTJSString\_S \*rawstr,
  tTJSString\_S \*seed) // seed=xp3hnp
{
  int v4; // edi
  int v5; // esi
  int (\_\_stdcall \*v6)(tTJSString\_S \*); // eax
  int rawstr\_len; // edi
  int (\_\_stdcall \*v8)(tTJSString\_S \*); // eax
  uint8\_t \*rawstr\_cstr; // eax
  int (\_\_stdcall \*v10)(tTJSString\_S \*); // eax
  int seed\_len; // edi
  int (\_\_stdcall \*v12)(tTJSString\_S \*); // eax
  uint8\_t \*seed\_cstr; // eax
  unsigned int saltsize; // \[esp-4h] \[ebp-54h]
  uint8\_t buf\[80]; // \[esp+0h] \[ebp-50h] BYREF
  saltsize = this->saltsize;
  qmemcpy(buf, "uespemosmodnarodarenegylsetybdet", 32);// hash outsize is 32
  dirhash\_init\_100172E0(buf, this->salt, saltsize);
  v6 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))tTJSString::length\_100AD158;
  if ( !tTJSString::length\_100AD158 )
  {
  v6 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))findfunc\_10016420((void (\_\_stdcall \*)(\_DWORD))aTjsIntTtjsstri);
  tTJSString::length\_100AD158 = (int)v6;
  }
  rawstr\_len = ((int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*, int, int))v6)(rawstr, v4, v5);
  v8 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4;
  if ( !TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4 )
  {
  v8 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))findfunc\_10016420((void (\_\_stdcall \*)(\_DWORD))aConstTjsCharTt);
  TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4 = (int)v8;
  }
  rawstr\_cstr = (uint8\_t \*)v8(rawstr);
  di rhash\_update\_10017480(buf, rawstr\_cstr, 2 \* rawstr\_len);
  if ( seed )
  {
  v10 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))tTJSString::length\_100AD158;
  if ( !tTJSString::length\_100AD158 )
  {
  v10 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))findfunc\_10016420((void (\_\_stdcall \*)(\_DWORD))aTjsIntTtjsstri);
  tTJSString::length\_100AD158 = (int)v10;
  }
  seed\_len = v10(seed);
  v12 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4;
  if ( !TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4 )
  {
  v12 = (int (\_\_stdcall \*)(tTJSString\_S \*))findfunc\_10016420((void (\_\_stdcall \*)(\_DWORD))aConstTjsCharTt);
  TJSString::c\_str\_100AD0F4 = (int)v12;
  }
  seed\_cstr = (uint8\_t \*)v12(seed);
  dirhash\_update\_10017480(buf, seed\_cstr, 2 \* seed\_len);
  }
  return dirhash\_final8\_10016BD0(buf, hashValueRet);// fill hashValueRet, return hash size
}
\`\`\`
看到这行诡异的字符串\`uespemosmodnarodarenegylsetybdet\`,一开始以为是key,结果并不是,他是init的参数立即数内联过来了。搜索\`0x736F6D6570736575\`,第一条就是\[siphash]\(https\://github.com/veorq/SipHash/blob/master/siphash.c)。
\`\`\` text
.text:100169F0 push ebp
.text:100169F1 mov ebp, esp
.text:100169F3 sub esp, 50h
.text:100169F6 push dword ptr \[ecx+8]
.text:100169F9 mov dword ptr \[ebp+buf], 70736575h
.text:10016A00 push dword ptr \[ecx+4]
.text:10016A03 lea ecx, \[ebp+buf]
.text:10016A06 mov dword ptr \[ebp+buf+4], 736F6D65h
.text:10016A0D mov dword ptr \[ebp+buf+8], 6E646F6Dh
.text:10016A14 mov dword ptr \[ebp+buf+0Ch], 646F7261h
.text:10016A1B mov dword ptr \[ebp+buf+10h], 6E657261h
.text:10016A22 mov dword ptr \[ebp+buf+14h], 6C796765h
.text:10016A29 mov dword ptr \[ebp+buf+18h], 79746573h
.text:10016A30 mov dword ptr \[ebp+buf+1Ch], 74656462h
\`\`\`
然后分析与上面类似,先写程序确定一下是不是常规的方法。经测试,文件夹哈希用了原版的\`siphash\_2\_4\`方案。
\`\`\`py
import siphash
h = siphash.SipHash\_2\_4(b"\x00" \* 16)
h.update("ED".encode("utf-16le"))
h.update("xp3hnp".encode("utf-16le"))
print(h.hexdigest()) # FEF68C92D344F4F6
\`\`\`
\## epilogue
好久没写逆向分析文章了,目前看除了我开源的\[krkr\_hxv4\_dumphash]\(https\://github.com/YuriSizuku/GalgameReverse/blob/master/project/krkr/src/krkr\_hxv4\_dumphash.cpp),没有公开的资料来具体分析这个臭名昭著的hxv4哈希函数,故写此文。写逆向游戏分析的文章不是想象中的那么容易,一写就是几个小时。因为分析游戏大多时间间隔很长,有时候卡住了往往要过几天才突然有灵感,有些关键地方可能突然想到了或者排查了半天刚好找到,整理并回顾这些过程也花了些时间。这些突破点往往不容易在文章里准确的表达,而且逆向本身也有很多很繁琐的流程,面面俱到都写进去反而使得文章冗长,整体流程不清晰。因此本文以分析哈希函数为主,其他部分仅写了关键流程和数据结构,略去了繁琐的调试过程,希望可以抛砖引玉,享受在逆向抽丝剥茧的乐趣中。
\## reference
\[krkrz]\(https\://github.com/krkrz/krkrz)
\[KrkrExtractForCxdecV2]\(https\://github.com/YeLikesss/KrkrExtractForCxdecV2)
\[krkrdump]\(https\://github.com/crskycode/KrkrDump)
\[hxcrypt]\(https\://github.com/crskycode/GARbro/blob/master/ArcFormats/KiriKiri/HxCrypt.cs)
\[krkr\_hxv4\_dumpkey]\(https\://github.com/YuriSizuku/GalgameReverse/blob/master/project/krkr/src/krkr\_hxv4\_dumpkey.js)
\[krkr\_hxv4\_dumphash]\(https\://github.com/YuriSizuku/GalgameReverse/blob/master/project/krkr/src/krkr\_hxv4\_dumphash.cpp)
\[blake2s]\(https\://github.com/secworks/blake2s/blob/master/src/model/blake2s.c)
\[siphash]\(https\://github.com/veorq/SipHash/blob/master/siphash.c)